Blog
Automation & AI in MedTech Technical Documentation
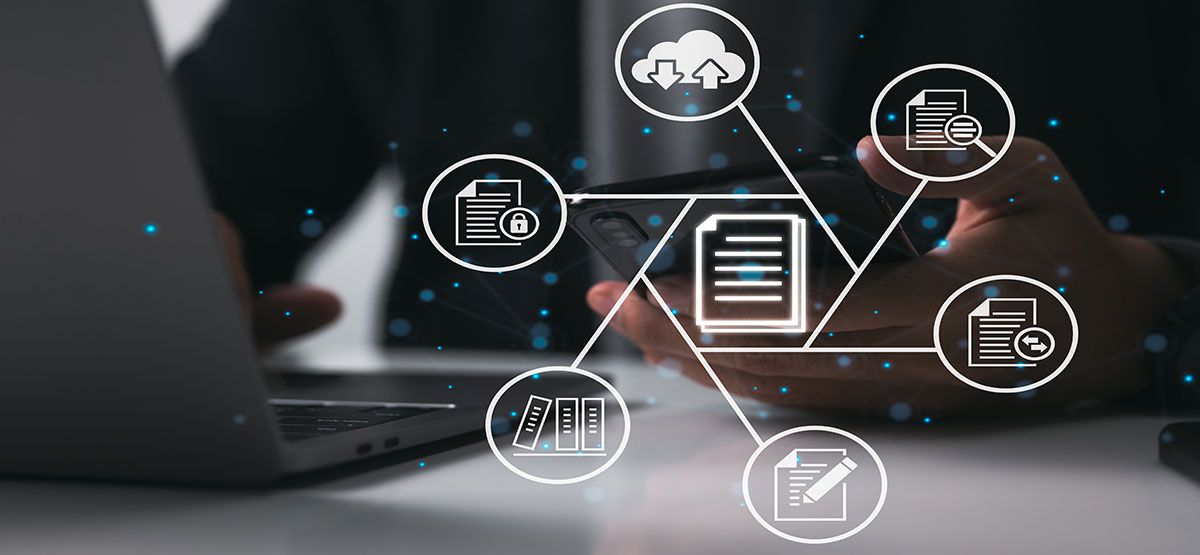
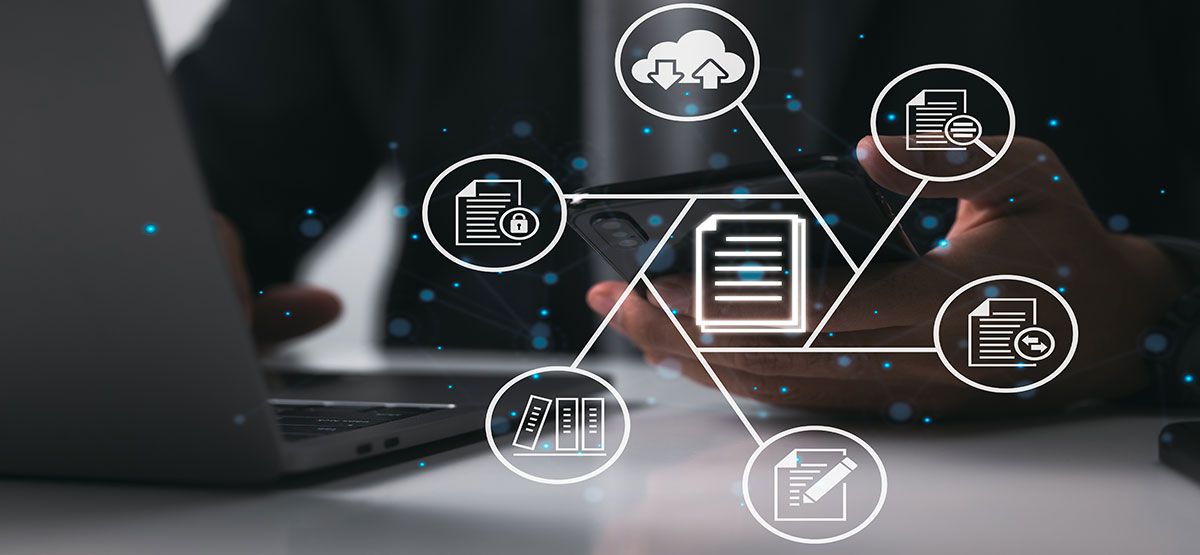
The medical device industry is in the midst of a digital revolution. From smart diagnostics to AI-powered monitoring systems, technology is transforming healthcare delivery at its core. But one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked in this digital transformation is the way regulatory documentation is created, managed, and submitted. For decades, regulatory submissions for medical devices involved mountains of paper files, manual data entry, and fragmented systems. Today, digitalization is streamlining this process, improving efficiency, accuracy, and compliance across the board.
So, what does this shift mean for stakeholders in the medical device industry – especially for regulatory affairs professionals, manufacturers, and auditors? This article dives deep into how digitalizing technical documentation is reshaping the landscape of medical device regulatory submissions.
Technical documentation is the backbone of any medical device approval process. It includes comprehensive data on the device’s design, manufacturing, performance, safety, risk management, clinical evaluations, labeling, and more. Regulatory bodies like the FDA (U.S.), MHRA (UK), and notified bodies under the EU MDR require this documentation to ensure that devices are safe, effective, and compliant with regulatory standards.
But traditional methods of handling this documentation pose serious challenges. Paper-based systems are prone to human error, difficult to update, and time-consuming to audit. Even electronic systems without integration or proper digital workflows can lead to inconsistencies and non-compliance.
Role of Digitalization/AI in Regulatory Affairs
Digitalization in this context refers to converting paper-based or analog processes into a digital format that is structured, searchable, and integrated across systems. It’s not just about scanning documents into PDFs; it involves the use of software platforms, databases, cloud storage, and AI tools to automate, validate, and manage technical documents more efficiently.
For instance, a digital document management system (DMS) allows companies to centralize their documentation, maintain version control, automate updates, and ensure traceability – all of which are essential for regulatory audits and inspections. When done right, digitalization enhances transparency, reduces human error, and shortens time to market.
Benefits of Digitalizing Technical Documentation
Digitalizing regulatory submissions brings several tangible benefits to medical device companies:
1. Improved Efficiency and Speed
Digitally managed documents can be accessed, edited, and shared across teams in real time. This leads to faster reviews, quicker approvals, and reduced time-to-market for new devices.
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency
With automation tools, data entry errors and redundant information are minimized. Changes made in one section of the document can automatically reflect across all linked documents, maintaining consistency.
3. Easier Collaboration
Digital platforms enable multiple stakeholders – engineers, regulatory specialists, QA teams, and management – to collaborate seamlessly, no matter where they are located.
4. Better Compliance and Audit Readiness
Digital systems offer audit trails, version history, and access logs, making it easier to prove compliance during audits or inspections.
5. Cost Reduction
Although the initial setup of digital tools may require investment, over time they significantly reduce the costs associated with printing, storing, and managing paper documents.
Challenges in Adopting Automation
Despite its benefits, digitalization is not without hurdles:
1. Resistance to Change
Many organizations are deeply entrenched in traditional processes. Convincing teams to adopt new digital tools can be met with skepticism and resistance.
2. Initial Investment
The cost of acquiring and implementing digital platforms can be high, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, the ROI justifies the expense in the long run.
3. Data Security and Privacy
Storing sensitive regulatory data digitally necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to prevent data breaches, especially when dealing with patient-related information or proprietary designs.
4. Training and Skill Gaps
Employees need to be trained on new systems, which takes time and resources. Bridging this skill gap is essential for successful digital transformation.
Key Components of Digital Technical Documentation
For digitalization to be effective, certain core components must be incorporated into the system:
1. Document Management Systems (DMS)
A robust DMS is the foundation of digital technical documentation. It offers secure storage, version control, approval workflows, and access management.
2. Electronic Signatures and Audit Trails
Regulatory bodies accept electronic signatures under standards such as FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11. These features ensure accountability and compliance, allowing traceability of who approved or modified documents and when.
3. Integrated Quality Management Systems (QMS)
Digital QMS platforms integrate with DMS, linking quality processes like CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions), complaints, and risk assessments directly with the corresponding technical documentation.
4. Cloud-Based Access
Remote access to technical documentation is increasingly important, especially with the global nature of teams and audits. Cloud solutions ensure real-time access while maintaining security and compliance.
5. Metadata and Searchability
Digitized documents with metadata tagging improve navigation and retrieval. Instead of sifting through paper files, users can perform quick searches to find relevant content instantly.
Regulatory Expectations for Digitalization
While digitalization is primarily driven by internal efficiency, it also aligns with the evolving expectations of regulatory authorities. Agencies are increasingly recognizing the legitimacy of digital documents and workflows, provided they meet strict criteria:
- Traceability – Clear records of who accessed or altered a document and when.
- Validation – Systems must be validated to prove they function correctly and consistently.
- Security – Protection against unauthorized access, data corruption, or loss.
- Retention – Documents must be preserved in a readable format for a defined period.
Although regulatory agencies vary in their digital readiness, the trend is moving toward greater acceptance of digital documentation, making early adoption a competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Implementing Digital Documentation Systems
Transitioning to a fully digital documentation system requires strategic planning. Here are some best practices:
1. Assess Current Workflows
Map out your existing document lifecycle – from creation to approval – and identify pain points or redundancies that digital tools can address.
2. Choose the Right Platform
Not all digital tools are created equal. Select platforms that are compliant with relevant standards, scalable, and user-friendly.
3. Pilot the System
Start with a pilot project involving a limited number of documents and users. This helps identify issues and fine-tune workflows before full-scale rollout.
4. Train Your Team
Conduct comprehensive training sessions to ensure that everyone understands how to use the new system and follows best practices.
5. Maintain Continuous Improvement
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your digital documentation system and make improvements based on feedback and audit findings.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Digital Transformation
Case Study 1: Medium-Sized Manufacturer in Europe
A mid-sized medical device company in Germany transitioned from paper-based documentation to a cloud-based DMS. The result? A 40% reduction in submission preparation time and a 60% decrease in audit non-conformities.
Case Study 2: U.S.-Based Startup
A U.S.-based startup leveraged digital tools from the beginning, integrating its QMS and DMS on a single platform. This streamlined their FDA 510(k) and ISO 13485 submission processes, helping them go to market 6 months ahead of schedule.
These examples illustrate that organizations of all sizes can benefit from embracing digitalization – so long as the transition is thoughtfully executed.
Conclusion
Digitalization of technical documentation in medical device regulatory submissions is no longer a futuristic concept – it’s a present-day necessity. It enhances efficiency, compliance, and collaboration while paving the way for faster innovation and safer patient outcomes. By moving away from paper-based processes and embracing integrated digital systems, medical device companies can not only meet today’s regulatory expectations but also future-proof their operations.
Digital transformation is not just about technology – it’s about mindset. Regulatory affairs teams that embrace change and invest in robust digital systems will lead the next wave of healthcare innovation.
If you are a medical device manufacturer or regulatory professional looking to streamline your documentation processes and accelerate approvals, DDi can help in digitalization to future-proof your compliance strategy.
Get the latest updates from DDi
Explore Topics
- Automation & AI (6)
- Clinical Automation (8)
- Consumer Health (1)
- IRT & Clinical Supplies (22)
- Labeling (16)
- Regulations (23)
- Regulatory Automation (14)
- Regulatory Biopharma (3)
- Regulatory Content Management (4)
- Regulatory Information Management (22)
- UDI (11)
- Writing (12)
Recent Blogs
 The Smarter Way to Manage…In Regulations
The Smarter Way to Manage…In Regulations Meeting Compliance with N…In IRT & Clinical Supplies
Meeting Compliance with N…In IRT & Clinical Supplies Pharma Workflows with Bus…In Regulatory Biopharma
Pharma Workflows with Bus…In Regulatory Biopharma
Previous Post
Next Post
Related Posts


CONNECT WITH US

Let's talk about how DDi can help you

